Table of Contents
Introduction
Clean a Car Radiator – here are the highlights of the steps taken about cleaning the car radiator: get rid of the old cooling water inside the radiator and ensure the car engine is excellent so the person can start working.
Wear rubber gloves and goggles to take into account public safety matters. Use the jack crane to lift the car’s front to access the radiator drain below.
Lift the hood and locate the radiator. Open the lid of the radiator above, which controls the pressure of the radiator. Next, open the drain plug below the radiator.
Ensure the entire radiator cooling water is discharged before re-stopping the drain below the radiator. Finally, clean the radiator from the inside: pour both cleaning material and distilled water into the radiator.
Turn on the engine for five minutes until the water and cleaning material heat up, take the cooling cycle inside the radiator, and reach all areas cleaned. Next, please turn off the engine and leave it for 15 minutes until it cools down.
Open the lid of the radiator and drain plug together to get rid of the cleaning material. Pour water into the radiator using a hose until it remains confirmed that the water coming out of the drain has become clean.
Refilling the refills with cooling water: mix approximately 2 liters of antifreeze with the same amount of distilled water. Add the mixture through the top cover of the radiator. Turn on the car’s engine to ensure that the antifreeze material has filled all cooling system parts (radiator). Continue to increase the mix until the radiator remains filled.
The Principle of the Work of the Radiator
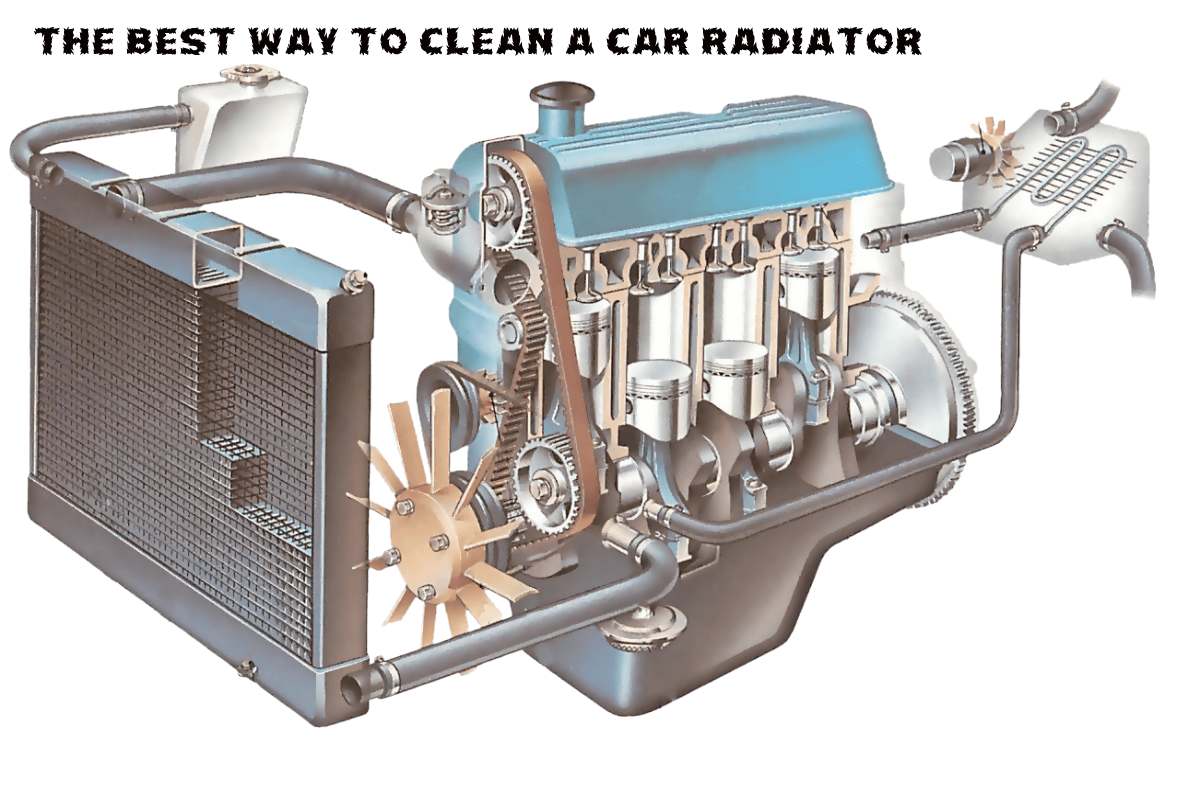
the importance of the radiator lies in the fact that it is considered the central part of the car responsible for eliminating the excess heat caused by the work of the engine while securing the cooling necessary for it through the coolant that passes inside it to reach the fan that expels that heat out of the car.
It remains known that most modern vehicles are made of aluminum in the form of small fins and structured tubes and fixed in parallel with each other passes the radiator, and the function of fins is limited to that when they are in contact with these hot pipes, they move the heat out of them.
Types of Radiators
here are the most prominent kinds of reeds used in cars: radiator pygmy pipes. This type of radiator is the oldest and used to date, with cooling water flowing into pipes, each with many circular rings (fins) pressed firmly on its outer surface.
Tube radiator distinguishes this species from its predecessor in that the pipes in this type do not have the surrounding fins from the outside, and the lines remain vertically arranged in a space made in the form of copper fins.
Radiator beehive the beehive radiator, also known as cellular recital (cell ratio), consists of many air cells surrounded by cooling water within specific corridors, so a blockage in any airway will have an effect limited to a small part of the total cooling system.
The Impact of Oil Shortage
Significant problems can occur due to the lack of oil in the engine. And the consequences of the shortage lead to catastrophic and severe implications for engine safety and performance.
The drought effects include increasing the friction between moving parts such as pistons and rotational deans. In addition, they grew combustion products from gases and scattered delicate metal parts—corrosion and rust exposure of metal engine elements. As a result, the engine is overheating, and its features are damaged.
Where is the Oil in the Engine?
The oil remains found in the basin called the Cartier that surrounds the crank column. With which the oils gather at the bottom. Engine oil is the nerve of the engine. Without which the vehicles will not work normally and adequately. As engine oil protects the engine of the car by lubricating the moving parts.
Therefore, the importance of oil crystallizes in reducing the temperature by reducing friction and is the engine’s biggest enemy Furthermore, since the oil becomes contaminated due to use. Following the manufacturer’s instructions and bulletins about the oil change period and the recommended oil quality.
Engine oil Function
Lubricant plays a vital role in the engine’s operation. As the lubrication system ensures that the oil reaches each moving part to enable it to function efficiently and smoothly.
These two elements are one of the essential elements in terms of its need for oil, the pistons so that they can easily slide into their cylinders non-stop. And the revolving columns such as crank and cam-shaft to complete the rotation freely.
In most cars, you can pump out the oil from the oil bowl or Cartier by the oil pump and then passes through the oil filter to remove Any harmful impurities. Then pumped under high pressure on the cylinder walls. The oil retreats back into the basin, where it is collected there again, and the cycle remains the same.